Trade-Based Money Laundering (TBML) is rapidly rising to the top of the agenda for both financial institutions and regulatory bodies, and for good reason. Unlike conventional money laundering techniques that may rely on straightforward layering, TBML conceals illicit funds behind the appearance of legitimate trade, exploiting discrepancies in invoicing, shipping, and documentation. This makes it one of the most sophisticated and opaque financial crime typologies to detect.
The challenge becomes even more pronounced in regions like the Middle East, where high trade volumes, free zones, and complex cross-border flows form a dense, fast-moving network of transactions. Traditional AML systems, often designed to detect more linear patterns of suspicious activity, often struggle to handle the layered datasets, fragmented counterparties, and increasingly adaptive methods TBML entails. In this environment, detecting financial crime is not just a matter of scanning transactions, it requires advanced analytics, trade document verification, and dynamic risk scoring powered by AI and data-driven compliance technologies.
What Is Trade-Based Money Laundering?
Trade-Based Money Laundering (TBML) is the process of disguising the proceeds of crime and transferring value through seemingly legitimate trade transactions. Rather than relying on traditional methods like cash smuggling or wire fraud, TBML leverages the complexity of international trade to obscure illicit financial flows within routine commercial activity.
Criminals exploit weaknesses in trade finance systems by manipulating documentation and shipment details. Common techniques include:
- Over- or under-invoicing – Inflating or deflating the value of goods to move funds illicitly
- Trade in dual-use goods – Using items that have both civilian and military applications to mask illicit purposes
- Multiple invoicing – Generating more than one invoice for a single shipment to justify repeated payments
- Over- or under-shipment – Mismatching declared quantities with actual shipments
- False descriptions of goods – Misrepresenting the nature or quality of items in trade documents
- Phantom shipments – Recording transactions for goods that were never actually shipped
The objective is clear: move illicit value without raising red flags within the financial system. Because the deception lies deep within logistics and documentation, areas often outside the scope of traditional AML monitoring, TBML can go undetected for extended periods.
In high-volume trade corridors like those in the Middle East, the risk is amplified due to fragmented oversight, multiple jurisdictions, and large-scale trade flows.
Why TBML Is So Difficult to Detect
What makes TBML particularly challenging to detect is its ability to blend seamlessly into the flow of legitimate global commerce. Transactions may appear entirely routine, with invoices, customs declarations, and shipping records all seemingly in order. This makes it exceptionally difficult to distinguish legitimate trade from sophisticated manipulation.
Most financial institutions do not have direct access to the underlying trade documentation, the physical verification of goods, or the credibility of all counterparties involved. Without this visibility, they are left to assess risk based on fragmented or second-hand data.
Compounding the challenge is the multi-layered nature of trade finance. A single transaction might involve exporters, importers, logistics providers, banks, insurers, customs brokers, and regulators, each governed by different jurisdictions, currencies, and regulatory expectations. This complexity creates blind spots that criminals can exploit.
Without integrated data systems and intelligent technology such as AI-driven document analysis and cross-border entity risk scoring, financial institutions are left relying on manual reviews that simply cannot match the scale, speed, or deception of modern TBML schemes
The Role of Technology in TBML Detection
Traditional AML systems often struggle to uncover trade-based laundering techniques. However, advanced AML platforms are increasingly closing this gap by leveraging artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data integration to bring clarity to complex trade environments.
By automating document analysis, mapping transactional behaviors, and correlating trade and payment data, modern AML technologies empower compliance teams to detect hidden patterns that were previously inaccessible.
The following table outlines key AI-powered capabilities and how they directly support TBML detection efforts:
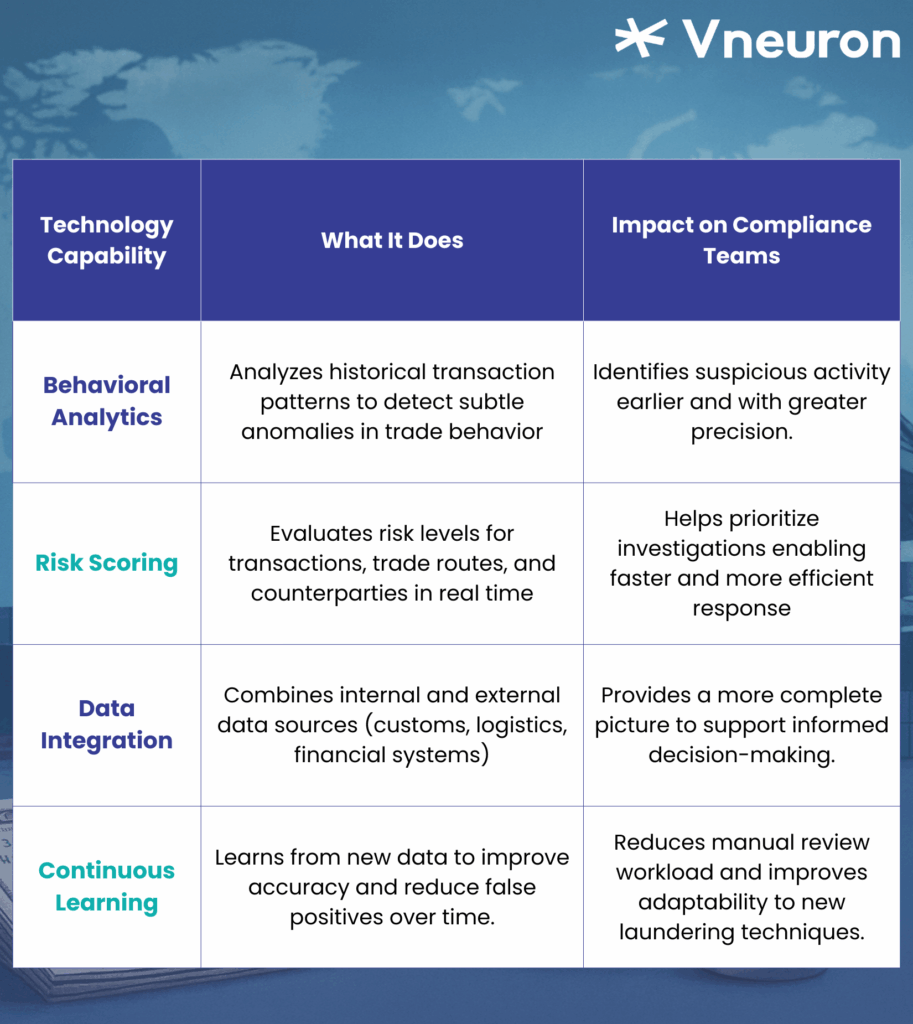
Why This Is Especially Relevant in the Middle East
With the Middle East expanding its global trade footprint and modernizing regulatory frameworks, regional compliance teams are under increasing pressure to detect more sophisticated risks like Trade‑Based Money Laundering (TBML). In the UAE, the National AML/CFT Strategy 2024–2027, approved by Cabinet in September 2024, explicitly prioritizes TBML as a high-risk vector, and places significant responsibility on banks to detect and deter such schemes
Against this evolving regulatory backdrop, AI and machine learning are becoming indispensable. These technologies enable compliance teams to analyze large volumes of trade, shipping, and payment data, automatically flagging irregularities such as invoice anomalies, mismatched shipment data, or non-physical “phantom” transactions.
Importantly, they offer the speed and scalability needed to align with increasingly rigorous supervisory expectations and enforcement trends
Final Thoughts
Trade-Based Money Laundering (TBML) remains a growing threat for institutions engaged in international trade. As regulatory expectations intensify and laundering tactics become more sophisticated, compliance teams require more than traditional controls. They need agile, intelligent, and data-driven solutions.
By adopting AI-powered platforms that integrate behavioral analytics, risk scoring, and cross-border data visibility, financial institutions can significantly enhance their ability to detect, investigate, and mitigate TBML risk.
Interested in seeing how it works?
Book a live demo with our experts to discover how Reis™ RCS by Vneuron equips your team with the tools to monitor trade activities more effectively, meet regulatory obligations, and stay one step ahead of financial crime.

