Crowdfunding's Dark Side: Unmasking Money Laundering Vulnerabilities
In the ever-expanding universe of financial technologies, crowdfunding has emerged as both a catalyst for innovation and a breeding ground for unforeseen risks. As of 2023, the global crowdfunding market has soared to a valuation of 1.41 billion U.S. dollars, a testament to its exponential growth. However, beneath the promising surface lies a shadowy undercurrent, accentuated by a statistic that foretells an impending storm: by 2030, the market is poised to more than double, boasting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.5 percent according to a study by Statista.
This flourishing ecosystem, while fostering creativity and entrepreneurial spirit, has become a magnet for an insidious foe: money launderers seeking to exploit the very mechanisms designed to democratize finance.
In this blog, we navigate the labyrinth of threats posed by money laundering in crowdfunding, the forms, and the technology’s role in preventing crowdfunding money laundering risks.
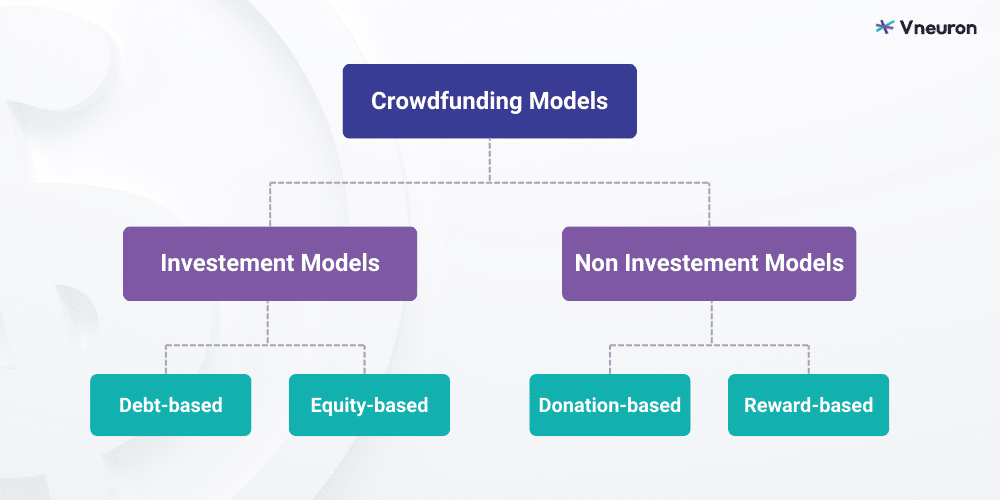
Defining crowdfunding and its types
Crowdfunding, a financial mechanism where a collective of backers funds projects or ventures, comes in various types, each offering unique dynamics.
1. Debt-based crowdfunding :
In debt-based crowdfunding, financial support takes the form of loans. Backers act as lenders, providing funds with an expectation of repayment with interest. This model enables businesses or individuals to secure capital while offering backers a tangible financial return on their investment.
2. Equity-based crowdfunding :
Redefining investment dynamics, equity-based crowdfunding grants backers ownership stakes. Investors become shareholders, aligning their interests with the venture’s success. This democratized investment approach fosters a sense of shared ownership and financial alignment.
3. Donation-based crowdfunding :
Donation-based crowdfunding relies on altruism, with backers contributing funds without expecting financial returns. This type is prevalent in charitable, social impact, and community projects. Backers are motivated by a sense of philanthropy, supporting causes that resonate with their values and beliefs.
4. Reward-based crowdfunding :
In this model, backers contribute funds motivated by non-monetary incentives. Projects entice supporters with rewards like exclusive products, early access, or personalized experiences. This type thrives on community engagement, transforming backers into advocates of the creative journey.
Overview of the crowdfunding for terrorism financing shared by the FATF in October 2023
The FATF’s October 2023 report outlines critical challenges in combatting terrorism financing through crowdfunding :
Challenges for platforms
- Lack of Expertise: Crowdfunding platforms often lack expertise in identifying terrorism-related fundraising activities due to a rapidly evolving industry.
- Reporting Gaps: Donation-based crowdfunding platforms, often outside AML/CFT regulations, lack sophisticated monitoring, hindering the identification of potential illicit activities.
- Fragmented Payments: Operating across various platforms and financial channels creates challenges in applying due diligence measures, with entities viewing themselves as intermediaries.
Challenges for authorities
- Proving intent: Establishing the intent behind crowdfunding transactions related to terrorism financing is complex, compounded by weak identification practices.
- Operational complexity: Involvement of multiple actors across jurisdictions complicates investigations, requiring specialized expertise.
- Lack of data: Insufficient data on the extent of crowdfunding misuse for terrorism financing hampers effective risk assessment.
- Anonymizing techniques: The use of encryption and anonymizing technologies adds complexity to investigations, making it challenging to obtain relevant information.
Best practices shared by the FATF in the report :
- Improve understanding: Conducting national risk assessments and understanding crowdfunding industry risks.
- Consider risk factors: Evaluating risk factors, including the use of virtual assets and the platform’s communications posture.
- Balance regulation: Regulating crowdfunding while ensuring innovation is not stifled.
- Encourage private sector efforts: Supporting private sector-led initiatives to strengthen industry practices, training, and compliance.
- Conduct outreach: Increasing awareness among reporting entities and private sectors to enhance AML/CFT compliance.
- Establish collaboration: Facilitating public-private collaboration for information exchange and detection of terrorism financing.
After exploring the challenges and best practices in combatting terrorism financing through crowdfunding shared by the FATF, it’s crucial to explore potential scenarios of money laundering. Understanding these scenarios is vital for developing effective countermeasures and ensuring the integrity of crowdfunding platforms in the face of evolving financial risks.
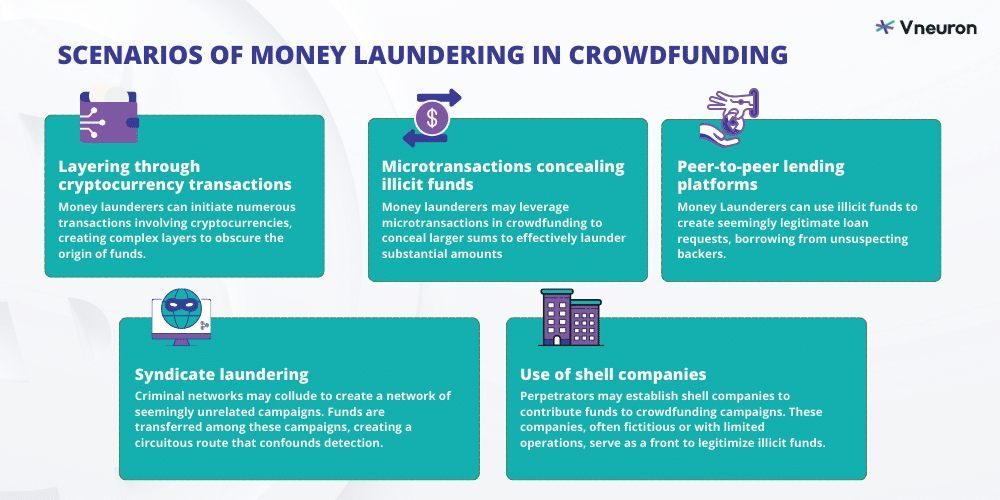
Scenarios of money laundering in crowdfunding
Layering through cryptocurrency transactions:
Money launderers may exploit the anonymity of cryptocurrencies in crowdfunding campaigns. They can initiate numerous transactions involving cryptocurrencies, creating complex layers to obscure the origin of funds. These transactions may involve multiple wallets and digital assets, making it challenging to trace the illicit funds.
Microtransactions concealing illicit funds :
Money launderers may leverage microtransactions in crowdfunding to conceal larger sums. By making numerous small contributions across various campaigns, they can effectively launder substantial amounts. This technique capitalizes on the decentralized nature of crowdfunding platforms, making it difficult for traditional AML methods to detect.
Use of shell companies:
Perpetrators may establish shell companies to contribute funds to crowdfunding campaigns. These companies, often fictitious or with limited operations, serve as a front to legitimize illicit funds. Crowdfunding platforms, which may have less stringent due diligence compared to traditional financial institutions, can become unwitting conduits for money laundering through these shell entities.
Syndicate laundering :
Criminal networks may collude to create a network of seemingly unrelated campaigns. Funds are transferred among these campaigns, creating a circuitous route that confounds detection. This syndicate laundering method relies on coordinated efforts to move money seamlessly through multiple projects, exploiting the diverse nature of crowdfunding initiatives.
Exploiting peer-to-peer lending platforms :
In debt-based crowdfunding, money launderers may abuse the lending model. They can use illicit funds to create seemingly legitimate loan requests, borrowing from unsuspecting backers. Once the funds are received, they may default on the loans or repay using other illicit funds, completing the laundering cycle through the peer-to-peer lending structure.
To proactively mitigate the risks of such scenarios, leveraging cutting-edge technology becomes indispensable. Advanced AML-TF technologies not only serve as safeguards but also empower financial institutions to maintain the highest standards of compliance.
Combatting money laundering through crowdfunding: advanced AML compliance technologies
Blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) :
- Immutable transaction records: Utilizing blockchain and DLT ensures transparency and immutability of transaction records. This prevents unauthorized alterations to financial data, fostering a trustworthy environment resistant to fraudulent activities.
- Smart contracts for automated compliance: Implementing smart contracts allows for the creation of self-executing compliance protocols. These contracts can automatically enforce predefined rules, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Machine learning and predictive analytics :
- Anomaly detection: ML algorithms analyze vast datasets to discern patterns and anomalies indicative of potential ML or TF. This proactive approach enables real-time identification and intervention in suspicious transactions.
- Predictive models for risk assessment: Advanced analytics models predict emerging risks, empowering financial institutions to stay ahead of evolving ML and TF tactics. Predictive analytics aids in anticipating and preventing illicit financial behavior.
Natural language processing (NLP) and text analysis :
- Automated monitoring of unstructured data: NLP algorithms process unstructured data from various sources, including news articles and social media. This enables institutions to monitor public sentiment and news for signs of potential illicit financial activities.
- Semantic analysis for enhanced due diligence (EDD): Text analysis tools with semantic capabilities enhance EDD processes by extracting nuanced information from textual data, aiding in comprehensive risk assessments.
Cryptocurrency tracking and analysis:
- Behavioral analysis of crypto transactions: Advanced technologies analyze behavioral patterns in cryptocurrency transactions, identifying anomalies that may indicate illicit activities within blockchain networks.
- Forensic analysis tools: Cryptocurrency forensic tools assist in tracing and visualizing the flow of funds within blockchain networks, aiding investigative efforts in uncovering the origins and destinations of potentially illicit transactions.
Automation in transaction monitoring and screening:
- Real-time transaction surveillance: Automated systems enable real-time transaction monitoring, rapidly flagging and investigating suspicious activities.
- Automated watchlist screening: Automation streamlines the screening process against watchlists, ensuring the swift identification of individuals or entities associated with illicit activities.
- Automated regulatory reporting: RegTech streamlines the often cumbersome regulatory reporting process. Automated reporting systems ensure compliance with diverse and dynamic AML and TF regulations, minimizing the risk of non-compliance.
Generative AI for risk scenarios and pattern recognition:
- Simulating risk scenarios: Generative AI models simulate diverse ML and TF risk scenarios, assisting in the creation of robust risk management strategies.
- Pattern Recognition for Unsupervised Learning: Generative AI algorithms excel in unsupervised learning, recognizing subtle patterns indicative of potential financial crimes without explicit programming.
Vneuron's strategic approach recommendations for crowdfunding AML compliance
Amidst the challenges of crowdfunding’s growth and its vulnerability to money laundering, Vneuron provides key strategies to enhance AML compliance. For effective navigation of these challenges, as a financial institution, you need to adopt the following proactive measures:
1. Holistic risk-based approach:
- Develop a nuanced understanding of the diverse crowdfunding models and their inherent risks.
- Tailor AML procedures to align with the unique characteristics of each crowdfunding type, prioritizing resources based on assessed risk levels.
- Periodically reassess and adjust risk mitigation strategies to stay agile in the face of evolving threats.
2. Advanced due diligence protocols:
- Strengthen due diligence processes by incorporating advanced identity verification technologies.
- Implement robust background checks on project creators and backers, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of their financial activities.
- Continuously update due diligence protocols to adapt to emerging money laundering tactics and enhance accuracy.
3. Collaborative information ecosystem:
- Establish secure channels for real-time information sharing on suspicious activities, creating a united front against money laundering.
- Actively participate in industry-wide initiatives that aim to enhance the collective resilience of the financial sector.
4. Continuous training and awareness:
- Instill a culture of vigilance and compliance through regular training programs for staff and stakeholders.
- Raise awareness about evolving trends in crowdfunding-related money laundering, emphasizing the importance of prompt reporting.
- Develop and disseminate educational resources to empower stakeholders with the knowledge needed to identify and combat illicit financial activities.
5. Technological synergy:
- Integrate AML compliance technologies into existing systems to enhance detection capabilities.
- Explore collaborative opportunities with other advanced technology providers to create a layered defense against multifaceted money laundering techniques.
- Foster a culture of technological agility, ensuring the continuous adaptation of systems to counter emerging threats.
6. Regulatory engagement and advocacy:
- Engage proactively with regulatory bodies to contribute insights on AML challenges specific to crowdfunding.
- Advocate for flexible and adaptive regulatory frameworks that balance innovation with robust AML compliance.
- Align internal policies with evolving AML regulations, demonstrating a commitment to compliance and risk mitigation.
7. Scenario-Specific Strategies:
- Develop targeted strategies to address specific money laundering scenarios prevalent in crowdfunding.
- Conduct regular scenario-based exercises to test the efficacy of implemented strategies and refine them based on evolving threats.
In the relentless surge of the global crowdfunding market, prioritizing AML compliance is no longer a choice but a necessity. Beyond merely comprehending the intricacies of diverse crowdfunding models, financial institutions must proactively fortify their defenses. This entails not just embracing, but mastering advanced technologies to ensure a robust shield against evolving financial threats.
Ready to fortify against money laundering? Contact Vneuron for advanced AML solutions tailored to crowdfunding’s dynamic landscape.

