Insurance companies AML compliance demystified: your guide to insurance integrity in Saudi Arabia
The insurance industry is a vital sector contributing significantly to Saudi Arabia’s economy and achieving the Saudi 2030 vision. However, this sector faces the growing threat of financial crimes, including money laundering and terrorist financing. Therefore, it is imperative for insurance companies in Saudi Arabia to establish robust anti-money laundering (AML) programs.
This comprehensive guide explores the intricate AML regulations in Saudi Arabia and provides an in-depth roadmap for insurance companies to ensure compliance and safeguard the industry’s integrity.
An overview of Saudi Arabia's AML compliance and combating the financing of Terrorism legislation
The Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA)
- The Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) serves as the central bank of Saudi Arabia and plays a crucial role in regulating and supervising the insurance industry. SAMA has introduced a comprehensive set of regulations and guidelines to counteract money laundering and the financing of terrorism within the insurance sector..
The Insurance Authority
- In a significant development for the insurance sector in Saudi Arabia, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia announced the establishment of the Insurance Authority in August 2023.
Aligned with the ambitions of the visionary Saudi Vision 2030 and the Financial Sector Development Program, the IA has been endowed with a spectrum of mandates, encompassing the full spectrum of responsibilities stipulated in the Cooperative Health Insurance Law and the Cooperative Insurance Companies Control Law.
The prevailing regulations, rules, and directives established in alignment with these laws will continue in force until the finalization of legal procedures pertaining to the forthcoming insurance draft law and its implementation.
The anti-money Laundering and combating the financing of terrorism (AML/CFT) law
- In 2017, Saudi Arabia passed the AML/CFT Law, a milestone piece of legislation aimed at preventing and combating money laundering and terrorist financing within the country.
- However, to keep pace with the ever-evolving landscape of financial crimes and to maintain a robust defense against money laundering and terrorism financing, Saudi Arabia undertook a notable update to its AML/CFT framework in 2021.This update signified the nation’s unwavering commitment to overcoming emerging threats and bolstering its financial ecosystem’s resilience.
- The 2021 update to the AML/CFT framework introduced a host of refinements and enhancements to the existing legislation, further empowering financial institutions, including insurance companies, to identify, prevent, and report suspicious activities effectively.
AML/CFT Regulations for Insurance Companies
- In addition to the overarching AML/CFT Law, SAMA has furnished insurance companies with detailed regulations specifically tailored to ensure compliance with AML/CFT measures. These regulations encompass a range of critical areas:
1. AML/CFT Governance
Insurance companies are mandated to establish a dedicated AML/CFT unit within their organizational structure. Furthermore, they must appoint a compliance officer responsible for overseeing AML/CFT measures and ensuring their effective implementation.
2. Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
Insurance companies are obligated to conduct thorough CDD on all customers, including policyholders, beneficiaries, and third-party payers. This process involves verifying the customer’s identity, understanding the nature of their business, and assessing the risk associated with the customer.
3. Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR)
Insurance companies are further required to report any suspicious activities to the Financial Investigation Unit (FIU) of SAMA. These activities include transactions that appear unusual, lack an apparent economic or lawful purpose, or are inconsistent with the customer’s profile.
4. Record Keeping
To maintain transparency and accountability, insurance companies must retain records of all transactions and customer information for at least five years. These records should be easily accessible and contain all necessary information for identifying the customer and understanding the nature of the transaction.
5. Training and Awareness
Regular training and awareness programs are essential. Insurance companies are required to provide comprehensive training for their employees. This training is designed to equip employees with a deep understanding of the importance of AML/CFT measures and their role in safeguarding the financial system. Topics covered include identifying suspicious activities, executing customer due diligence, and understanding the reporting procedures.
Now, having laid the groundwork with an understanding of the law and legislation surrounding insurance companies in KSA, it is essential to delve into the practical implementation of AML/CFT measures.
AML compliance for insurance companies in 5 steps :
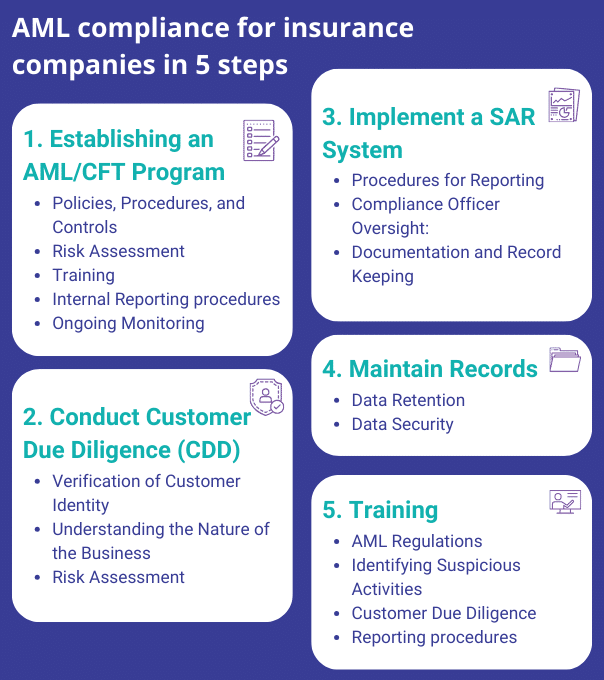
1. Establishing an AML/CFT Program
The initial step for insurance companies to ensure compliance with AML regulations is to establish an AML/CFT program. This program should encompass a range of critical elements, including:
- Policies, Procedures, and Controls: The program should encompass well-defined policies, procedures, and controls, designed to identify and mitigate the risks associated with money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Risk Assessment: A thorough risk assessment should be conducted to pinpoint high-risk areas and customers.
- Training: Employees should be provided with the necessary training to understand their roles and responsibilities within the AML/CFT program.
- Internal Reporting Mechanisms: Establishing clear internal reporting mechanisms will ensure that compliance teams can report suspicious activities promptly.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Implementing a continuous monitoring process is key to detecting any unusual patterns or behaviors.
2. Conduct Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
Insurance companies in Saudi Arabia are mandated to conduct CDD on all customers, as per the regulations. The CDD process should include the following:
- Verification of Customer Identity: The KYC (Know Your Customer) Module is pivotal in the CDD framework, serving as a cornerstone for verifying customer identities. Equipped with sophisticated verification processes, it cross-checks customer data with credible sources, ensuring a robust validation process with a heightened level of certainty. This module integrates state-of-the-art tools such as advanced document scanning, facial recognition, and biometric verification, enabling a comprehensive and secure validation of customer identity.
- Understanding the Nature of the Business: Understanding the nature of the customer’s business activities is a vital element of CDD. A dedicated Business Profiling Module is essential to create comprehensive profiles of customer enterprises. Analyzing business documents, financial statements, and transaction patterns, provides insights into the legitimacy of a customer’s commercial operations. Moreover, it enables the identification of red flags and unusual business activities that may warrant further scrutiny.
- Risk Assessment: To meet the stringent requirements of AML compliance, the Risk Assessment Module is indispensable. This module employs advanced algorithms to assess the risk associated with each customer. It takes into account various risk factors, including geographical location, transaction volume, and the nature of the business. Based on the risk assessment, the insurance companies can identify the appropriate level of due diligence required for each customer, ensuring that AML efforts are focused on high-risk entities while expediting the process for low-risk customers.
3. Implement a Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR) System
The implementation of a well-structured SAR system is crucial. This system should include:
- Procedures for Reporting: Precisely defined procedures should be put in place to guide employees through the process of reporting any suspicious activities they may encounter. For insurance companies, this includes identifying transactions or behaviors that deviate from established norms or exhibit characteristics that suggest potential money laundering or terrorist financing. The procedures should be designed to ensure prompt and comprehensive reporting, with clear guidelines on what constitutes suspicious activity.
- Compliance Officer Oversight: Appointing a dedicated compliance officer is an essential step. This individual assumes the pivotal role of overseeing and managing the SAR process within the insurance company. Their responsibilities encompass the review, validation, and submission of SARs to the Financial Investigation Unit (FIU). This role is instrumental in ensuring that SARs are meticulously prepared, meeting regulatory requirements, and maintaining the necessary documentation.
- Documentation and Record Keeping: A robust SAR system entails the meticulous maintenance of comprehensive documentation associated with reported suspicious activities. These records serve as a vital audit trail, facilitating regulatory compliance and internal assessments. For insurance companies, this documentation may include transaction records, customer information, and any supporting evidence that led to the suspicion.
4. Maintain Records
Effective record-keeping stands as a critical pillar of AML compliance for insurance companies. To meet regulatory requirements, insurers are obliged to maintain records of all transactions and customer information for a minimum of five years.
These records should be easily accessible and encompass all essential details necessary for customer identification and transaction comprehension. It is imperative to prioritize data retention, ensuring that all pertinent data, including transaction specifics and customer information, is securely stored and readily accessible for audits and compliance verifications. Additionally, implementing stringent data security measures is vital to safeguard the stored information from unauthorized access and potential breaches, upholding the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive data.
5. Provide Training and Awareness Programs
Regular training and awareness programs are essential to ensure that employees are equipped with the knowledge and skills required for AML/CFT compliance. The training programs must cover different topics, including AML regulations, customer due diligence, reporting, transaction monitoring and screening, etc.
Insurance companies employees must be well-prepared to report any suspicious activities they may encounter in their roles.
To optimize AML compliance within financial institutions, a strategic integration of technology is imperative. This entails the seamless fusion of advanced technological solutions into the core AML framework.
The Technological Paradigm: Algorithms, Automation, and Advanced Technologies in AML Compliance for Insurance Companies in KSA
In the intricate landscape of anti-money laundering (AML) compliance for insurance companies in Saudi Arabia (KSA), cutting-edge technology takes center stage. Beyond regulatory mandates, the essence of effective AML implementation lies in the algorithms, automation, and advanced technologies at the core of this critical endeavor.
This section dives deep into the technological underpinnings that empower AML compliance and the importance of investing in these digital assets for insurance companies in KSA.
Harnessing Algorithmic Intelligence
Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics:
The heart of modern AML compliance beats with machine learning algorithms. These algorithms can discern patterns in massive datasets and predict potentially illicit activities. By analyzing historical transaction data, machine learning models can identify anomalies and outliers, facilitating the early detection of suspicious behavior.
Behavior-Based Models:
Algorithms can be trained to recognize the behavioral patterns of customers and transactions. Through continuous monitoring, they become adept at distinguishing normal from abnormal behavior. This technology is crucial for insurers, as it minimizes false positives and focuses attention on genuine threats.
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP algorithms can sift through vast amounts of unstructured data, including news articles and social media, to identify emerging risks and threats. Insurance companies can leverage NLP to stay ahead of trends and anticipate potential AML challenges.
The Automation Advantage
Transaction Monitoring
Automation streamlines the process of real-time transaction monitoring. It enables insurance companies to apply consistent scrutiny to all transactions, identifying suspicious ones instantly and, when necessary, suspending them. This not only prevents money laundering but also ensures regulatory compliance.
Customer Due Diligence (CDD):
Automated AML compliance tools simplify customer onboarding. They can quickly verify identities, cross-reference customer data with watchlists, and determine the level of risk associated with each customer. This expedites the CDD process and reduces the administrative burden on employees.
SAR Reporting:
Generating Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) is often an arduous and error-prone task. AML compliance solutions automate this process, ensuring that SARs are correctly compiled, submitted, and stored. The software provides an audit trail, enhancing transparency and accountability.
Advanced Technologies Leading the Way
Big Data Analytics:
AML Compliance solutions powered with big data analytics enable insurers to harness vast amounts of structured and unstructured data. This data can be used to gain deep insights into customer behavior, detect hidden risks, and optimize AML processes.
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Leveraging AI-driven algorithms, insurers can swiftly detect suspicious activities by analyzing transaction data for anomalies.
Moreover, AI-powered risk assessment models expedite decision-making by evaluating various factors, such as transaction volumes and business nature, ensuring effective allocation of AML resources to high-risk areas. The integration of AI technologies enhances the precision and responsiveness of AML efforts, bolstering the sector’s defense against financial crimes.
Automation and Robotic Process Automation (RPA):
Automation technologies are revolutionizing AML compliance by streamlining repetitive tasks and ensuring consistent, error-free processes. RPA, in particular, excels in automating data entry, report generation, and compliance checks. By reducing manual intervention, insurers can enhance efficiency and reduce the risk of human error.
What to consider when choosing an AML compliance solution for your insurance company
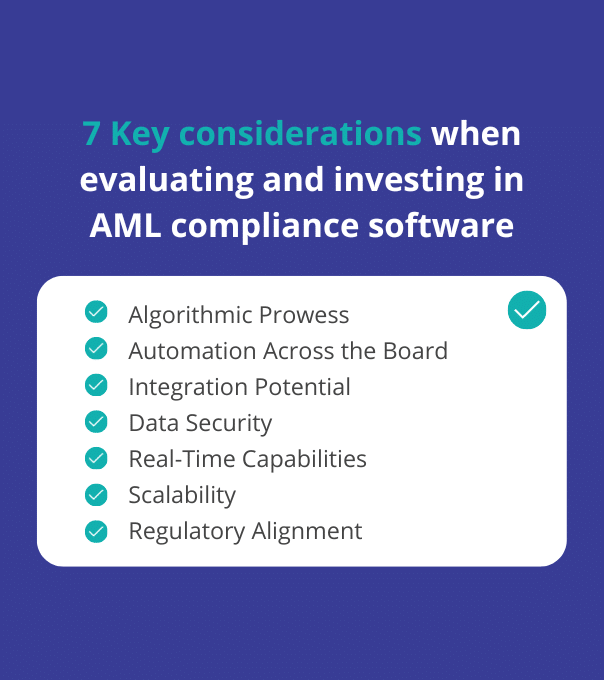
When insurance companies in KSA seek to strengthen their AML compliance programs, they must look beyond the regulatory checklist and consider the technological backbone of their operations. Here are key considerations when evaluating and investing in AML compliance software:
- Algorithmic Prowess: Select software and tools with robust machine learning capabilities. Look for algorithms that evolve over time and adapt to changing threats.
- Automation Across the Board: Ensure that the technology you choose can automate various aspects of AML compliance, from transaction monitoring to reporting and customer due diligence.
- Integration Potential: Seek solutions that seamlessly integrate with your existing systems. AML technology should enhance, not hinder, your operational efficiency.
- Data Security: As you embrace advanced technologies, data security becomes paramount. Choose solutions with advanced encryption and cybersecurity features to safeguard sensitive information.
- Real-Time Capabilities: Prioritize technology that operates in real-time. AML compliance requires swift action, and real-time monitoring and alerts are essential.
- Scalability: The chosen technology should scale with your insurance business. As your operations grow, the technology should accommodate increasing data volumes and processing requirements.
- Regulatory Alignment: Ensure that the technology is designed to comply with international regulations and the specific regulations of the Saudi Arabian insurance industry.
The path to robust AML compliance for insurance companies in Saudi Arabia is not merely a matter of ticking regulatory boxes, but a dynamic, technology-driven imperative. As the insurance industry in the Kingdom faces the ever-evolving landscape of financial crimes and emerging threats, embracing cutting-edge technology becomes paramount.
Vneuron, as a leading AML compliance technology provider, is dedicated to supporting insurance companies in Saudi Arabia in their quest for effective compliance. Our advanced Risk and Compliance Suite is designed to meet the specific needs of the insurance industry, aligning perfectly with the AML/CFT framework and the regulations set forth by SAMA.
Want to know more about our offering? Book a demo now, our specialists will be happy to answer all your questions!

